Python avanzado¶
Context managers¶
with¶
>>> with open('context.txt', 'w') as f:
... f.write("You don't need to close...")
...
...
26
>>> f.closed
True
Generadores¶
Generadores: yield¶
>>> def my_gen():
... yield 2
... yield 1
...
>>> for n in my_gen():
... print(n)
...
2
1
>>> list(my_gen())
[2, 1]
>>> g = my_gen()
>>> next(g)
2
>>> next(g)
1
>>> next(g)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
StopIteration
Generadores: yield¶
>>> def fib():
... a, b = 0, 1
... while True:
... yield b
... a, b = b, a + b
...
>>> f = fib()
>>> f
<generator object fib at 0x...>
>>> next(f)
1
>>> next(f)
1
>>> next(f)
2
>>> next(f)
3
>>> next(f)
5
Generadores en builtin functions¶
>>> range(3)
range(0, 3)
>>> for n in range(3):
... print(n)
...
0
1
2
>>> d = [0, 1, 2, 3]
>>> r = reversed(d)
>>> for k in r:
... print(k)
...
3
2
1
0
>>> for k in r:
... print(k)
>>>
>>> def is_even(x): return x % 2 == 0
>>> d = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
>>> even = filter(is_even, d)
>>> for k in even:
... print(k)
...
0
2
4
>>> for k in even:
... print(k)
>>>
También map.
Ejemplo completo¶
Inicializar generador con un argumento
Recibir parámetro
>>> def multiply_by(k):
... n = 1
... while True:
... msg = yield k * n
... n += 1
... if msg:
... print(f"Llevamos {n} iteraciones")
>>> double = multiply_by(2)
>>> double.__next__()
2
>>> double.send(False)
4
>>> double.send(True)
Llevamos 3 iteraciones
6
>>> next(double)
8
Funciones¶
Funciones: polimorfismo¶
def catch_all(*args, **kwargs):
print('Args: ', args)
print('Kwargs: ', kwargs)
>>> catch_all()
Args: ()
Kwargs: {}
>>> catch_all(1, 2)
Args: (1, 2)
Kwargs: {}
>>> catch_all(1, 2, a=1)
Args: (1, 2)
Kwargs: {'a': 1}
Funciones: parámetros especiales¶
def f(pos1, pos2, /, pos_or_kwd, *, kwd1, kwd2):
----------- ---------- ----------
| | |
| Posición o Clave |
| - Clave solo
-- Posición solo
def standard_arg(arg):
print(arg)
def pos_only_arg(arg, /):
print(arg)
def kwd_only_arg(*, arg):
print(arg)
def combined_example(pos_only, /, standard, *, kwd_only):
print(pos_only, standard, kwd_only)
def func(a, b, /, *, double=False):
rv = a * b
if double:
rv = 2 * rv
return rv
>>> func(3, 4)
12
>>> func(3, 4, double=True)
24
>>> func(3, 4, True)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: func() takes 2 positional arguments but 3 were given
>>> func(b=4, a=3, double=True)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: func() got some positional-only arguments passed as keyword arguments: 'a, b'
Cadenas de documentación¶
def foo():
"""What this function does."""
return
>>> foo.__name__
'foo'
>>> foo.__doc__
'What this function does.'
Decoradores¶
Decoradores¶
>>> def entry_exit(fn):
... def new_fn():
... print('Enter', fn.__name__)
... fn()
... print('Exit', fn.__name__)
... return new_fn
...
>>> def greet():
... print('Hello')
...
>>> greet_decorated = entry_exit(greet)
>>>
>>> greet()
Hello
>>> greet_decorated()
Enter greet
Hello
Exit greet
Decoradores: sintaxis simplificada¶
>>> @entry_exit
... def greet():
... print('Hello')
...
>>> greet()
Enter greet
Hello
Exit greet
Decoradores: ejemplo completo¶
>>> from functools import wraps
>>> def my_decorator(f):
... @wraps(f)
... def wrapper(*args, **kwds):
... print('Calling decorated function')
... return f(*args, **kwds)
... return wrapper
...
>>> @my_decorator
... def example():
... """Docstring"""
... print('Called example function')
...
>>> example()
Calling decorated function
Called example function
>>> example.__name__
'example'
>>> example.__doc__
'Docstring'
Context manager¶
Context managers propios¶
from contextlib import contextmanager
@contextmanager
def message():
print('Start')
try:
yield
finally:
print('and end')
>>> with message():
... n = 1000
... while n > 0:
... n -= 1
Start
and end
Otras expresiones¶
Expresión lambda¶
>>> f = lambda: 1
>>> f()
1
>>> f = lambda x: 2 * x
>>> f(2)
4
Operador ternario¶
'Allowed' if age >= 18 else 'Forbidden'
Recetas e idioms¶
Interpolación de cadenas¶
>>> print('Hello %s!' % 'world')
Hello world!
>>> print('%(language)s has %(number)03d quote types.' %
... {'language': "Python", "number": 2})
Python has 002 quote types.
Formateado de cadenas¶
str.format(*args, **kwargs)
>>> '{0}, {1}, {2}'.format('a', 'b', 'c')
'a, b, c'
>>> '{}, {}, {}'.format('a', 'b', 'c')
'a, b, c'
>>> '{2}, {1}, {0}'.format('a', 'b', 'c')
'c, b, a'
>>> '{0}{1}{0}'.format('abra', 'cad')
'abracadabra'
>>> 'Coordinates: {latitude}, {longitude}'.format(
... latitude='37.24N', longitude='-115.81W'
... )
'Coordinates: 37.24N, -115.81W'
F-strings¶
>>> name = "Miguel"
>>> print(f"{name}")
Miguel
Desempaquetado¶
Devolver varios valores de una función
def division(a, b):
quotient = a // b
remainder = a % b
return quotient, remainder
>>> division(42, 8)
(5, 2)
>>> q, r = division(42, 8)
>>> q
5
>>> r
2
Desempaquetado: swap¶
>>> a, b = 1, 42
>>> a, b
(1, 42)
>>> a, b = b, a
>>> a, b
(42, 1)
Desempaquetado: resto¶
>>> toys = ['Buzz', 'Rex', 'Bo', 'Hamm', 'Slink', ]
>>> first, *rest = toys
>>> first
'Buzz'
>>> rest
['Rex', 'Bo', 'Hamm', 'Slink']
list comprehension¶
Sintaxis compacta
Rendimiento óptimo
fib = [1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21]
even = []
for n in fib:
if n % 2 == 0:
even.append(n)
even = [n for n in fib if n % 2 == 0]
dict comprehension¶
toys = ['Buzz', 'Rex', 'Bo', 'Hamm', 'Slink', ]
len_map = {}
for toy in toys:
len_map[toy] = len(toy)
len_map = {toy: len(toy) for toy in toys}
Generator expression¶
>>> fib = [1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21]
>>> even = (n for n in fib if n % 2 == 0)
>>> print(even)
<generator object <genexpr> at 0x...>
>>> list(even)
[2, 8]
Trabajo con secuencias: enumerate¶
enumerate(sequence, start=0)
>>> colores = ['rojo', 'amarillo', 'verde']
>>> list(enumerate(colores))
[(0, 'rojo'), (1, 'amarillo'), (2, 'verde')]
>>> list(enumerate(colores, 1))
[(1, 'rojo'), (2, 'amarillo'), (3, 'verde')]
Trabajo con secuencias: range¶
range(stop) o range(start, stop[, step])
>>> range(10)
range(0, 10)
>>> list(range(10))
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> list(range(1,11))
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
>>> list(range(0, 30, 5))
[0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25]
Trabajo con secuencias: sorted¶
sorted(iterable[, key[, reverse]]])
>>> toys = ['Buzz', 'Rex', 'Bo', 'Hamm', 'Slink', ]
>>> sorted(toys) # Alphabetic
['Bo', 'Buzz', 'Hamm', 'Rex', 'Slink']
>>> sorted(toys, key=len) # length
['Bo', 'Rex', 'Buzz', 'Hamm', 'Slink']
>>> sorted(toys, key=lambda x: x[1]) # second char alphabetic
['Hamm', 'Rex', 'Slink', 'Bo', 'Buzz']
Trabajo con secuencias: zip¶
zip([iterable, ...])
>>> words = ['uno', 'dos', 'tres']
>>> numbers = [1, 2, 3]
>>> zip(words, numbers)
<zip object at 0x...>
>>> list(zip(words, numbers))
[('uno', 1), ('dos', 2), ('tres', 3)]
>>> list(zip(range(1000), 'abcdef'))
[(0, 'a'), (1, 'b'), (2, 'c'), (3, 'd'), (4, 'e'), (5, 'f')]
Trabajo con secuencias: unzip¶
>>> z = [('uno', 1), ('dos', 2), ('tres', 3)]
>>> list(zip(*z))
[('uno', 'dos', 'tres'), (1, 2, 3)]
>>> words, numbers = zip(*z)
>>> words
('uno', 'dos', 'tres')
>>> numbers
(1, 2, 3)
Excepciones¶
Herencia de excepciones¶
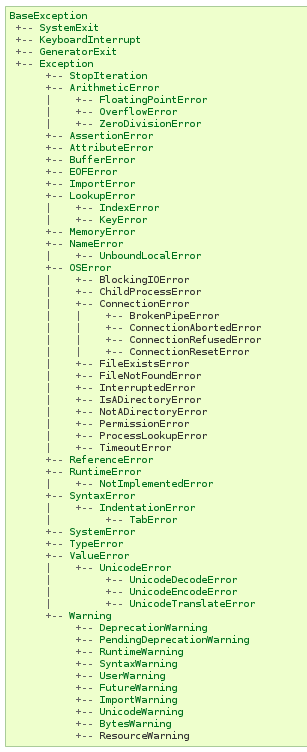
Herencia de excepciones (1)¶
BaseException
+-- SystemExit
+-- KeyboardInterrupt
+-- GeneratorExit
+-- Exception
Herencia de excepciones: Exception¶
+-- Exception
+-- StopIteration
+-- ArithmeticError
+-- AssertionError
+-- AttributeError
+-- BufferError
+-- EOFError
+-- ImportError
+-- LookupError
+-- MemoryError
+-- NameError
+-- OSError
+-- ReferenceError
+-- RuntimeError
+-- SyntaxError
+-- SystemError
+-- TypeError
+-- ValueError
+-- Warning
Excepciones¶
exception ImportErrorSe lanza cuando no consigue encontrar un módulo o un nombre.
exception SyntaxErrorError de sintaxis en la escritura del programa.
exception KeyErrorNo encuentra la clave al acceder a un diccionario.
exception IndexErrorEl índice es incorrecto en una lista o tupla.
exception UnicodeErrorProblemas en la conversión de o hacia Unicode.
exception ValueErrorError genérico producido porque el valor recibido, aunque tiene el tipo correcto, tiene un valor inesperado.
exception TypeErrorLa operación o función no se puede aplicar a ese tipo.
exception KeyboardInterruptSe lanza cuando se interrumpe la ejecución de un programa después de pulsar las teclas Control-C.
Creación de excepciones propias¶
Es posible crear excepciones propias. Para ello basta crear una clase que
herede de Exception.
class ErrorPersonalizado(Exception):
pass